A Comprehensive B2B E-Commerce Approach to Integrated Business Planning and Operations: Converging e-Commerce, ERP, and CRM Systems
In the fast-paced world of manufacturing, small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) face the relentless challenge of staying competitive while ensuring operational excellence. By adopting a comprehensive approach to integrated business planning and operations that converges e-commerce, ERP, and CRM systems, businesses can proactively address challenges and stay ahead of the competition. Furthermore, when SME manufacturers adopt a well-integrated B2B e-commerce solution, they optimize operational efficiency, ensuring streamlined operations and exhibiting agility in response to market dynamics. Dive in with us as we explore the benefits of this integrated approach across diverse operational areas.
1. Product Development & Innovation:
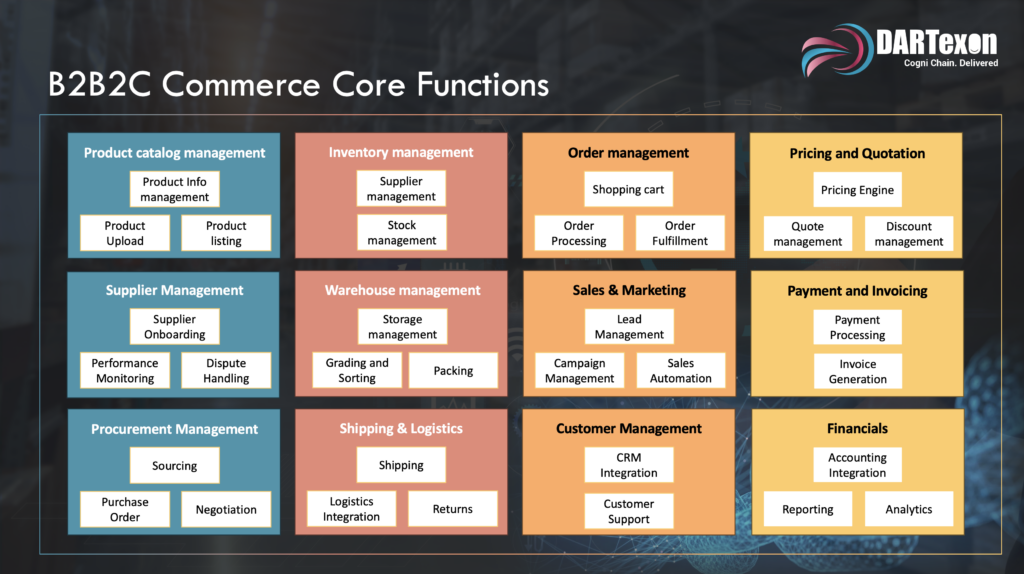
- Product Catalog Management: SME manufacturers can centralize their product data using ERP systems. By displaying accurate and consistent product information on e-Commerce platforms, these businesses can effectively engage potential customers and build trust.
- Research & Development: CRM tools, by capturing precise customer feedback, combined with ERP-driven analytics, can fuel product innovation. These insights guide the R&D team in developing products that resonate with market demands.
2. Sourcing & Procurement:
- Supplier Management: Establishing a robust relationship with suppliers is crucial for SMEs. SRM systems offer platforms to store vendor data, ensuring consistent and efficient communication.
- Sourcing & Procurement: Evaluating potential suppliers for quality and cost-efficiency, managing purchase order creation and tracking, and negotiating favorable contract terms and prices enabled by ERP systems.
- Purchase, Inventory, and MRP Management: ERP systems provide SMEs with a comprehensive overview of raw material stocks, aiding in the efficient planning of procurement and production schedules.
3. Order Fulfillment & Delivery:
- Order Management: Seamless order placements and prompt processing are achievable through e-Commerce platforms, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Shipping & Logistics: Integration with logistics partners ensures real-time shipping insights and punctual deliveries, fostering customer trust.
- Warehouse Management: Efficient organization and storage of goods, ensuring timely retrieval and dispatch to meet order demands, enabled with automated asset tracking and inventory control through RFID Technology.
- Payment and Invoicing: Secure payment gateways in e-Commerce platforms and ERP-driven automated invoicing streamline financial transactions.
4. Financial & Risk Management:
- Financials: Integrating ERPs with accounting tools offers SMEs real-time financial insights, aiding in strategic planning and resource allocation.
- Risk Management: ERP analytics can pinpoint operational vulnerabilities, enabling SMEs to devise strategies to counter potential disruptions.
5. Sales, Marketing & Client Relations:
- Sales & Marketing: With integrated e-Commerce platforms, SME manufacturers can widen their market reach, tapping into new customer bases.
- Pricing and Quotation: Dynamic pricing engines on e-Commerce platforms, combined with CRM’s quote management capabilities, allow SMEs to offer competitive and tailored pricing to clients.
- Customer Management: Using CRM tools, SMEs can delve deep into customer preferences, ensuring that their marketing strategies and product offerings align with client expectations.
6. Organization & Collaboration:
- Human Resources & Workforce Management: ERP and CRM integrations can oversee employee training, certifications, and productivity, ensuring an efficient workforce.
- Collaboration & Communication: Effective internal communication is the backbone of operational success. Integrated systems enhance cross-departmental collaboration, ensuring all teams work in unison.
7. Compliance, Quality, & Sustainability:
- Quality Control & Compliance: ERP modules can schedule quality inspections and ensure products adhere to industry standards and regulations.
- Environmental and Sustainability Metrics: By tracking the environmental impact of manufacturing processes via ERP systems, SMEs can adopt sustainable and eco-friendly practices.
In conclusion, to thrive in the ever-evolving manufacturing landscape, SMEs must embrace a holistic approach, integrating e-Commerce, ERP, and CRM systems across their operational domains. Such an integrated strategy ensures cohesive organizational goals, agile market responses, and streamlined operations – essential for sustained growth and competitiveness.
If you’re looking to transform your operations from isolated and tiresome Excel sheets to a comprehensive and integrated off-the-shelf product, reach out to us. We’re here to help elevate your business to the next level.